DIAGNOSTIC SERVICES
Cytogenetics / Karyotyping
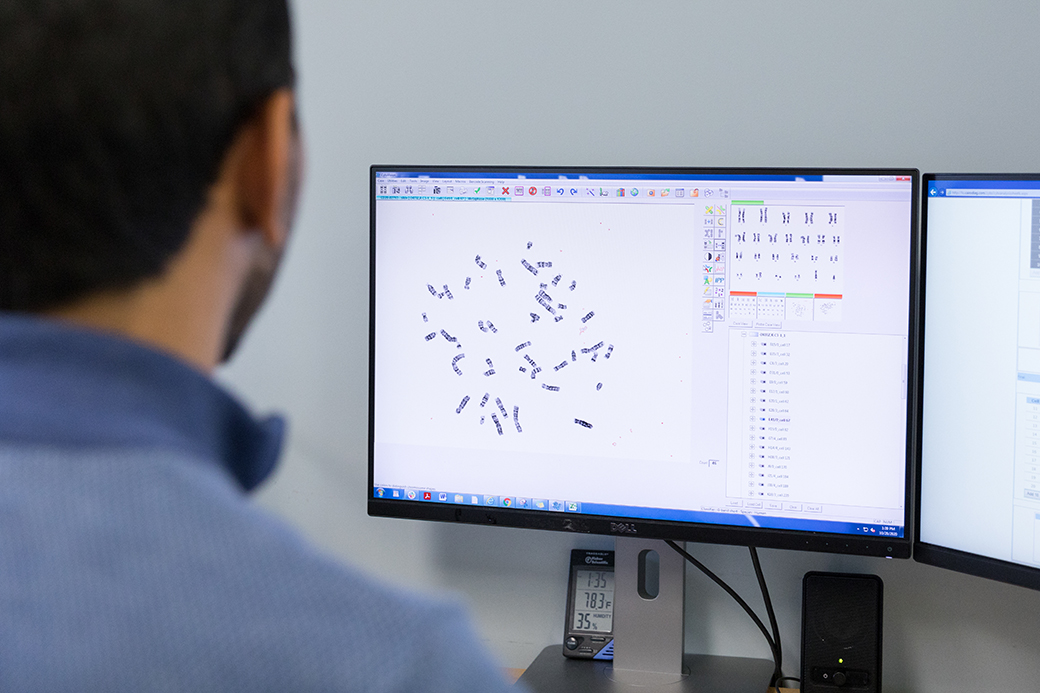
Karyotyping, also called whole genome chromosomal analysis, can differentiate primary and secondary changes; can address why, how, when and where chromosome abnormalities arise. Thus provide insights into diagnosis, prognosis, and prediction of disease in many acute and chronic leukemias and lymphomas. Traditional G-banding for at least 20 metaphase analyses with specific cell culturing and analyzed by two independent ASCP certified Cytogenetic Technologist ensures optimal results.
Turnaround time 3-5 days
Over 99% culture success
Cell-specific culture
- Myeloid Disorders
- B-Lymphoid Disorders
- T-Lymphoid Disorders
- Myeloma
FISH
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) is a molecular cytogenetic method, and works as an adjunct to karyotype analysis for the detection of cytogenetic abnormalities. FISH can help provide clarification of G-banded abnormalities or identify cryptic abnormalities not visible by karyotype analysis. The main advantages of FISH include: high sensitivity and specificity, rapid turnaround time, capacity to analyze large numbers of cells, and ability to obtain adequate data from samples with a low mitotic index or terminally differentiated cells. Also, dividing cells are not required for FISH analysis using both fresh tissue and paraffin embedded tissue.
In general, two hundred interphase cells are analyzed per probe by two independent ASCP certified Cytogenetic Technologist (100 cells/reader).
FISH is most useful when the analysis is targeted toward specific translocation, rearrangement and gain or loss that are known to be associated with a particular disease. We offer the following Disease-focused FISH panels with the best-in-industry turnaround time (1-2 days )
Turnaround time 2 days
Same day results for STAT cases
Complete suite of hematopoietic FISH probes
Disease-focused panels for
Hematologic FISH PANELS
| All |
| ABL1/BCR (9Q34.1/22Q11.2) |
| MLL (11q23) |
| ETV6ba (12p13.2) |
| IGH ba (14q32.3) |
| AML |
| D5S23,D5S721/EGR1 (5p15.2/5q31) |
| CEP 7/D7S522 (7p11.1/7q31) |
| RUNX1T1/RUNX1 (8q21.3/21q22) |
| MLL (11q23) |
| PML/RARA (15q24/17q21.1-21.2) |
| CBFB (16q22) |
| CLL |
| CCND1/IGH (11q13.2/14q32.3) |
| CEP 12 (p11.1-q11) |
| D13S319 (13q14.3)/LAMP1 (13q34) |
| ATM (11q22.3) |
| TP53 (17p13.1) |
Lymphoma
| HIGH GRADE LYMPHOMA |
| BCL6 ba (3q27) |
| MYC ba (8q24.21) |
| IGH/BCL2 (14q32.3/18q21.3) |
| CML |
| ABL1/BCR (9q34.1/22q11.2) |
| EOSINOPHILIA |
| PDGFRA (4q12) |
| PDGFRB (5q32) |
| FGFR1 (8p11.23-p11.22) |
| PCM1/JAK2 (8p22/9p24.1) |
| MDS |
| D5S23,D5S721/EGR1 (5p15.2/5q31) |
| CEP 7/D7S522 (7p11.1-q11.1/7q31) |
| CEP 8 (p11.1-q11.1) |
| ETV6 (12p13.2) |
| TP53 (17p13.1)/CEP 17(17p11.1q11.1) |
| D20S108 (20q12) |
| T-CELL LYMPHOMA |
| CEP 7/D7S522 (7p11.1/7q31) |
| IGH ba (14q32.2) |
| MYC/IGH/CEP 8 (8q24.2/14q32.3/8p11.-q11.1) |
| MM |
| 1pTEL/p58(1p36)1q25 |
| FGFR3/IGH (4p16.3/14q32.3) |
| CEP 9 (p11-q11)/CEP 15 (p11.2)/ TP53 (17P13.1) |
| CCND1/IGH (11q13.3/14q32.3) |
| D13S319 (13q14.3)/LAMP1 (13q34) |
| IGH ba (14q32.3) |
| IGH/MAF (14q32.3/16q23) |
| IGH/MAFB (14q32.3/20q12) |
| MPN |
| ABL1/BCR (9q34.1/22q11.2) |
| CEP 8 (P11.1-q11.1) |
| ETV6 ba (12p13) |
| D13S319 (13q14.3)/LAMP1 (13q34) |
| D2OS319 (20q12) |
| MARGINAL ZONE LYMPHOMA |
| CEP3 (3p11.1-q11.1) |
| MYB (6q23.2-q23.2) |
| CEP 7/D7S522 (7p11.1-q11.1/7q31) |
| CCND1/IGH (11q13.2/14q32.2 |
| BIRC3/MALT1 (11q22.1/18q21.3) |